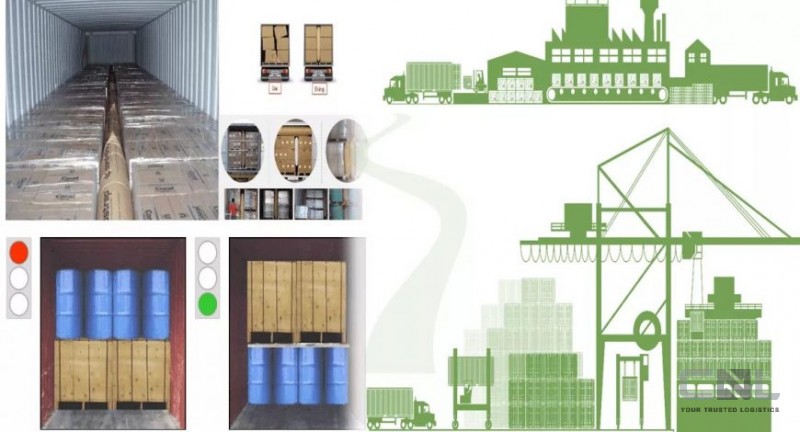
PRINCIPLE 1: CLEAN THE CONTAINER, DEODORIZE BEFORE LOADING THE CONTAINER
There are many items that are smelly, and a lot of warehouses require very carefully about the smell and the container must be clean to be allowed to pack into the container.
To remove odors in containers, there are many different ways such as:
- Sweep, use soap to wash the container -Use coffee powder spread evenly from front to back of the container - Use a bunch of incense (incense) to
burn-Open the container door from the time the container
is picked up to the time the
truck moves to the warehouse
PRINCIPLE 2: HEAVY GOODS LINED UP UNDER LIGHT LINES LINED UP ABOVE
This is the first basic principle to remember. When stacking packages on top of each other, apply and gradually increase in height and weight for the packages located below.
For homogeneous packaging, the pressure capacity of the packaging is limited. Therefore, it is necessary to pay great attention when stacking packages on top of each other, ensuring that the bearing capacity of the bottom bales is always within the permissible level.
This principle extends further, if liquid packages are stacked in drums or wine barrels, they will be stacked above solid solid packages
PRINCIPLE 3: LARGE-SIZED PACKAGES ARE RANKED BELOW
Usually large sized goods will weigh more than small sizes, then will return to principle 1. However, the key point here is the bearing point and the convenience of loading and unloading.
For packages of the same material as all packed in cartons, wooden crates. Then the large package below, the small package above will be easy in loading and unloading operations.
The large package is located below, the small package is located above will make the most of the queue space. Restrictions are broken due to movement of goods in containers.
PRINCIPLE 4: DO NOT PLACE INCOMPATIBLE ITEMS IN THE SAME CONTAINER
Incompatible items as antagonistic items. One item harms the other, reducing the quality or spoiling each other.
For example: Seeds are placed together with vegetables, seeds have hygroscopic properties, vegetables escape moisture very strongly, seeds that absorb moisture a lot are the cause of germination even cancer. Or like putting coffee and medicine in the same container, both of these goods have a very strong smell and odor absorption ability together, which will reduce the quality and smell of each other.
If you want to put items of a taboo nature together in the same container, it is necessary to separate them by packaging and have to be stacked separately and with partitions.
But we recommend that it should not be because in the process of transporting containers, most of them are in a state of movement and swaying. Goods that are prone to tearing or damaging packaging will interfere with the nature of the goods spreading to other items.
For taboo goods, we give typical pairs as follows:-Group of hygroscopic goods:
Seeds, sugar, salt, cement, cereals of all kinds ...
-Group of goods radiating moisture: Fresh vegetables, bottled foods (beer, wine, ..) if broken, wood-Group
of foods radiating and smelling: Coffee, tobacco, onions, garlic, chemicals of all kinds.
Most living animals should not be kept together during transportation, if they do not eat each other, then they also lead to each other.
-Group of goods that emit dust, easy to get dirty: Powders of all kinds of bagging (cement, flour), paints, lubricants.
Group of cavalier, easily dirty goods: Electronic equipment, machinery and equipment, vehicles, fabrics ...
PRINCIPLE 5: EVEN WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION FROM THE END OF THE CONTAINER TO THE END OF THE CONTAINER
This principle directly affects the transportation of containers on the road and affects the loading and unloading of containers at the port. And affects the bearing capacity of the container case.
Loading up containers does not necessarily require perfect calculations for weight distribution. However, when packing, the goods must be evenly spread from front to back of the container door.
When loading a container with both heavy and light cargo, it is recommended to queue heavy below and heavy goods above. It is not recommended to load a heavy cargo and then lightly queue on this will skew the container load.
The consequences caused by the uneven distribution of tonnage on containers are as follows:
Changing the center of gravity of the container causes the container to overturn during transportation.
Deviating from the center of gravity of the container causes the container loading crane to be "locked" due to load deviation. For modern shore cranes, there will be a "lock" crane when the container is offloaded.
Container damage: Broken flooring, crooked container.
Damage to goods: Closing the load order will likely damage the goods. The load deflection is the closing of the row to one end as opposed to the light row or the void will. Heavy cargo will shift in case the bucket or loading wave impacts the light cargo.
PRINCIPLE 6: THE PRINCIPLE OF PACKING GOODS INTO REFRIGERATED
CONTAINERS Packing must create ventilation so that the flow of cold air circulates from front to back of the container. Do not overstock the red line above.
Adhere to the packing guidelines stated above.
Check that the car air conditioner and air conditioner are working properly.
Set the temperature, ventilation in accordance with the required technique for the item to be closed.
It is recommended to pack the goods at the required temperature into the container. It is not recommended to pack goods with insufficient temperature into containers, easily damaged goods.
PRINCIPLE 7: LIGATURES, INSERTION OF CARGO LINERS IN CONTAINERS
The insertion of cargo liners is the most important thing to note. Because, in the process of transporting goods, there is always a state of kinetic energy. Inertial retention always exists latent in the goods if there are no ligaments tying the goods to break down.
For goods that are machinery and equipment, insertion is a must. However, for goods that are pallets or cartons, the insertion is often ignored.
There is a case where the most common breakage is when opening the container door. This is the most common situation. When transporting goods is shifted towards the tail of the container and leans against the container door. When the container door opens, it is also time for the goods to fall.
PRINCIPLE 8: CHECK AND TAKE PICTURES OF GOODS, CONTAINERS, SEALS BEFORE AND AFTER PACKING.
It is necessary to inspect the container before packing, whether the container is eligible for packing. Sanitary conditions, technical conditions, conditions on the condition of new containers old and damaged.
There are ways to check the container before packing as follows:-Check if the container is dangling or not:
Open the container door, go in and close the container door. If a ray of light passes, the container is dangling.
-Open the container door to check if there is a smell.
-Bend down, look under the container floor to check if the container momentum is broken or not.
-Check whether the rubber gasket at the container is torn, broken or not.
-Check whether the door latches are welded, chiseled or not.
-Check the number of seals right or wrong.
Source: Door to Door Viet - tancang-stc.vn